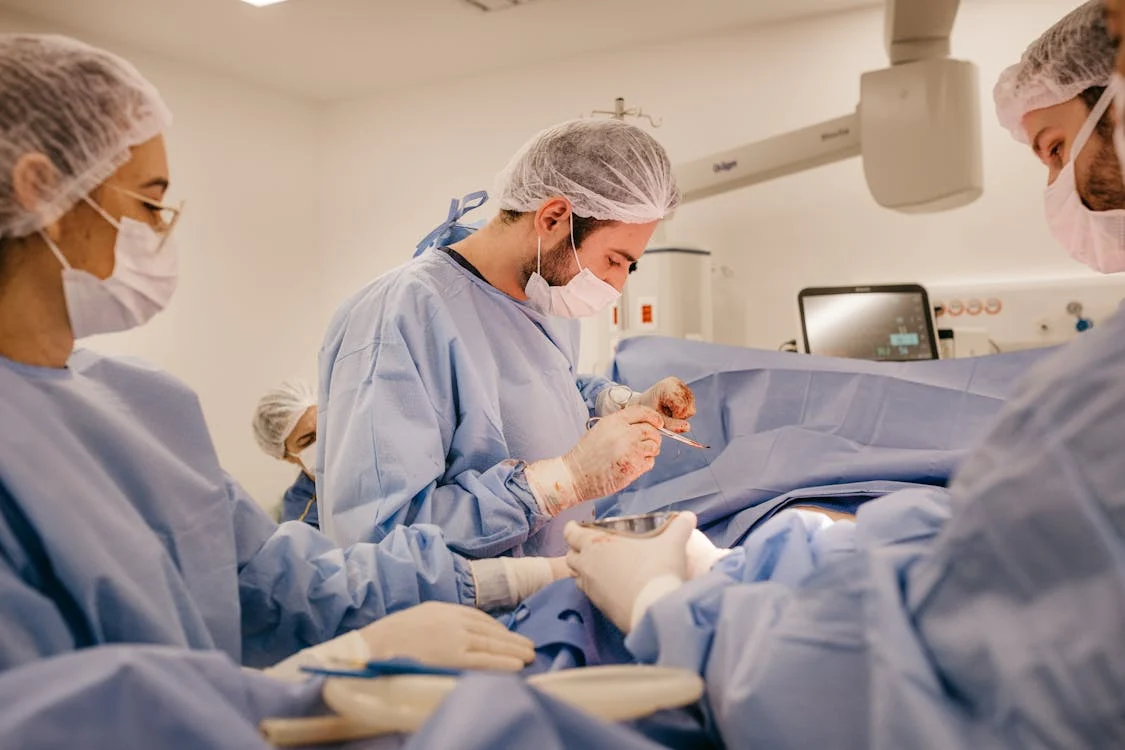
Hip mobility is crucial for everyday activities, from walking and climbing stairs to more active pursuits like sports. However, when issues like arthritis, fractures, or congenital conditions affect the hip joint, they can significantly impair mobility and quality of life, often necessitating hip surgery for effective treatment.
Understanding Hip Problems
Many people experience hip problems at some point in their lives, with arthritis being one of the most common culprits. This degenerative condition causes pain, stiffness, and inflammation in the hip joint, eventually leading to deterioration of cartilage. In severe cases where conservative treatments fail to provide relief, hip surgery becomes a viable option to restore mobility and alleviate pain.
Types of Hip Surgery
Hip Replacement Surgery:
Hip replacement surgery is a common procedure for severe arthritis or hip fractures. During this surgery, damaged parts of the hip joint are replaced with artificial components made from metal, ceramic, or plastic. Total hip replacement involves replacing both the ball and socket of the hip joint, while partial hip replacement involves replacing only the damaged part.
Hip Arthroscopy:
Hip arthroscopy is a minimally invasive procedure used to diagnose and treat various hip joint problems, including labral tears and femoroacetabular impingement (FAI). It involves inserting a small camera (arthroscope) into the hip joint through tiny incisions to visualize and repair damaged tissues without fully opening the joint.
Minimally Invasive Surgery:
Advancements in medical technology have led to the development of minimally invasive hip surgery, which offers smaller incisions, reduced muscle damage, and quicker recovery times compared to traditional open surgeries. This approach is suitable for select patients and conditions, providing similar outcomes with less surgical trauma.
Preparing for Hip Surgery
Before undergoing hip surgery, thorough preparation is essential. This typically begins with consultations with orthopedic specialists who assess the severity of the hip condition and discuss treatment options. Pre-operative preparations include physical examinations, blood tests, and imaging scans to ensure the patient is medically fit for surgery and to plan the procedure accordingly.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Post-operative care plays a crucial role in the success of hip surgery. Immediately after surgery, patients are monitored in the hospital for pain management and to prevent complications. Rehabilitation starts soon after, focusing on regaining strength, flexibility, and mobility through physical therapy exercises tailored to each patient’s needs and recovery timeline.
Alternative Treatments and Therapies
While hip surgery is often necessary for significant hip joint problems, there are alternative treatments and therapies that can complement or delay the need for surgery. Lifestyle modifications such as weight management, low-impact exercises, and dietary changes can help reduce symptoms and maintain hip joint health. Additionally, therapies like acupuncture, chiropractic care, and corticosteroid injections may provide relief from pain and inflammation associated with hip conditions.
Takeaway
Hip surgery represents a crucial treatment option for individuals suffering from debilitating hip joint issues. Whether it’s through hip replacement surgery, arthroscopy, or minimally invasive techniques, restoring mobility and alleviating pain can significantly enhance one’s quality of life. If you’re experiencing persistent hip pain or mobility issues, consulting with a healthcare professional is the first step towards understanding your options and finding a suitable treatment plan.