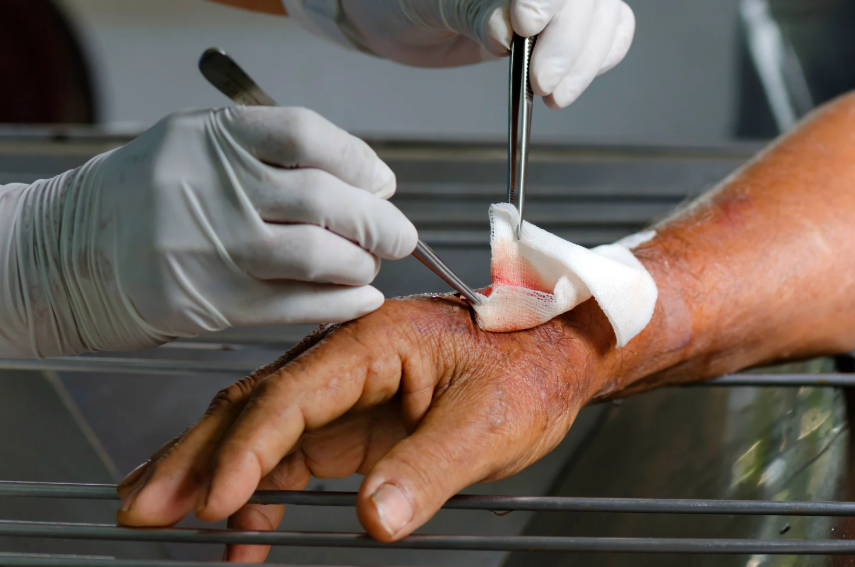
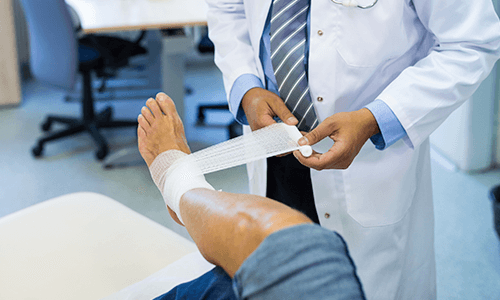
Orthopedic treatment for infected wounds is crucial in preventing complications that may arise from untreated infections. When wounds become infected, they can lead to severe pain, tissue damage, and even systemic infections. Without proper orthopedic treatment for infected wounds, patients may experience delayed healing, increased discomfort, and the risk of long-term mobility issues. Understanding the best practices in managing infection and pain effectively is essential for successful recovery.
Understanding Orthopedic Infections and Wound Healing
Orthopedic treatment for infected wounds involves addressing infections that occur due to surgical procedures, trauma, or underlying medical conditions such as diabetes. These infections often develop when bacteria enter a wound, leading to redness, swelling, pus formation, and fever. Without prompt orthopedic treatment for infected wounds, the infection can spread, affecting deeper tissues and bones. Proper wound healing requires early intervention, infection control, and appropriate pain management.
Diagnosing Infected Orthopedic Wounds
Early and accurate diagnosis is a key component of orthopedic treatment for infected wounds. Orthopedic specialists assess the wound by checking for common symptoms such as increased warmth, persistent pain, and foul-smelling discharge. Diagnostic methods include wound cultures to identify bacteria, blood tests to detect infection markers, and imaging techniques like X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans to evaluate the extent of the infection. By diagnosing infections early, orthopedic treatment for infected wounds can be more effective in preventing serious complications.
Treatment Strategies for Infected Wounds
Antibiotic Therapy for Infection Control
A fundamental aspect of orthopedic treatment for infected wounds is the use of antibiotics to eliminate bacterial infections. Depending on the severity, doctors may prescribe oral or intravenous antibiotics to target the specific bacteria causing the infection. In some cases, orthopedic treatment for infected wounds requires long-term antibiotic therapy to prevent recurrence. Patients should complete the prescribed course to ensure full eradication of the infection.
Surgical Debridement and Wound Cleaning
For severe cases, surgical debridement plays a crucial role in orthopedic treatment for infected wounds. This procedure involves removing dead or infected tissue to promote healing. Techniques such as sharp debridement, enzymatic debridement, and vacuum-assisted closure (VAC) help cleanse the wound and improve recovery outcomes. Orthopedic treatment for infected wounds with debridement is particularly beneficial for patients with deep infections or slow-healing wounds.
Pain Management for Orthopedic Wounds
Managing pain is a significant part of orthopedic treatment for infected wounds. Patients may receive pain relief through medications like NSAIDs, opioids, and topical anesthetics. Non-drug approaches, including cold therapy, compression, and physical therapy, also contribute to effective pain management. Since infection-related pain can be severe, a comprehensive pain management strategy is essential in orthopedic treatment for infected wounds.
Advanced Treatment Options for Severe Infections
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT)
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is an advanced method used in orthopedic treatment for infected wounds. This therapy increases oxygen supply to the affected area, accelerating wound healing and reducing bacterial growth. HBOT is especially beneficial for patients with chronic infections or slow-healing wounds, enhancing the effectiveness of standard orthopedic treatment for infected wounds.
Skin Grafts and Tissue Reconstruction
For extensive tissue damage, skin grafts and tissue reconstruction are important components of orthopedic treatment for infected wounds. Surgeons transplant healthy skin to cover the wound, promoting faster healing and reducing the risk of further infections. This method is particularly useful when large portions of skin and soft tissue are affected by infection.
Bone Infections (Osteomyelitis) Treatment
When infections spread to the bones, orthopedic treatment for infected wounds becomes more complex. Osteomyelitis, a severe bone infection, requires long-term antibiotic therapy, surgical debridement, or even bone grafting. Early detection and aggressive treatment are necessary to prevent permanent bone damage and disability.
Preventing Orthopedic Wound Infections
Prevention is a key focus in orthopedic treatment for infected wounds. Proper wound care, including regular cleaning and dressing changes, significantly reduces infection risks. Patients should follow hygiene protocols, avoid contaminating the wound, and attend follow-up appointments with their orthopedic specialists. Additionally, lifestyle choices such as proper nutrition, hydration, and smoking cessation play a role in supporting wound healing and preventing infections.
Takeaway
Effective orthopedic treatment for infected wounds ensures timely infection control, pain relief, and proper healing. By seeking professional care, patients can prevent complications, recover faster, and maintain mobility. Prioritizing orthopedic treatment for infected wounds is essential for long-term health and well-being. If you or a loved one is experiencing signs of an infected wound, consult an orthopedic specialist to receive the best care and prevent further complications.