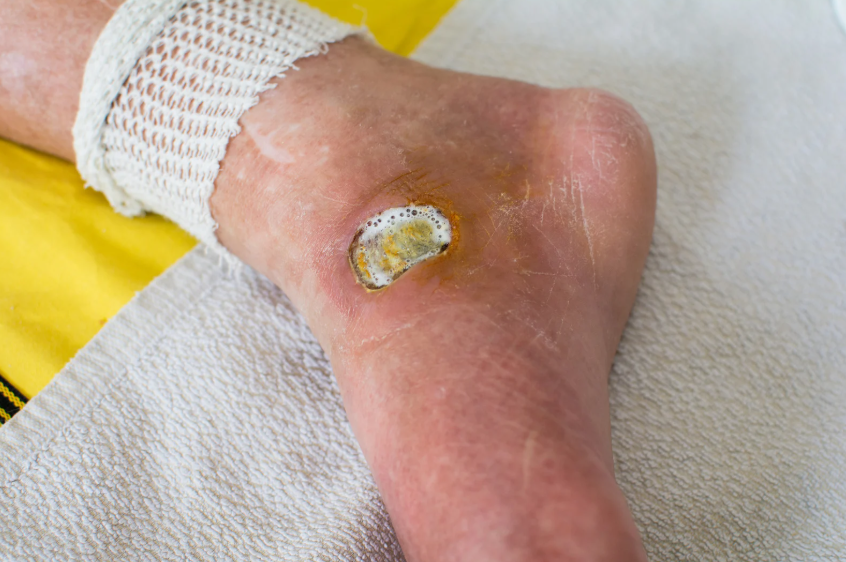
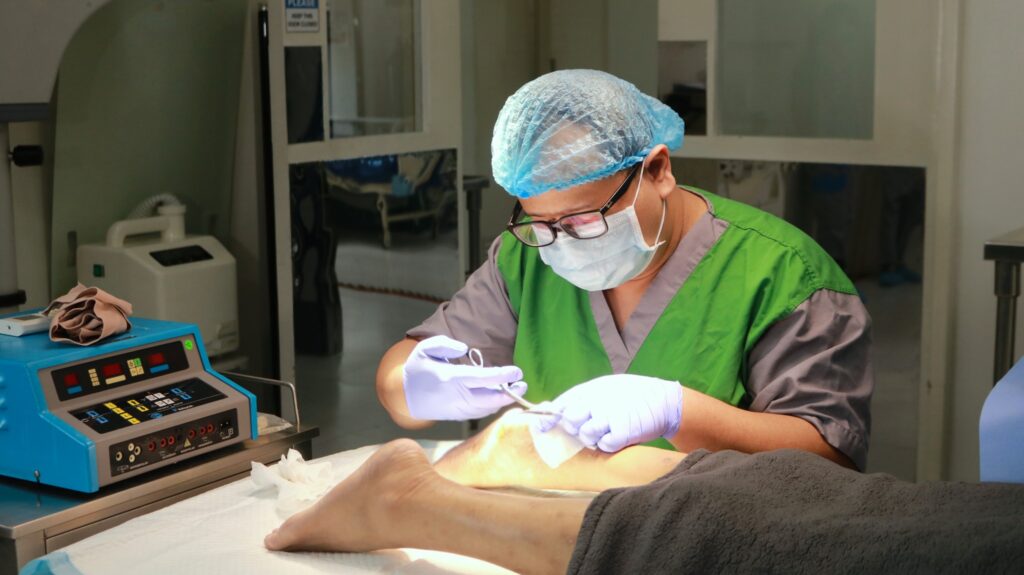
Diabetic gangrene is a severe complication that arises due to prolonged high blood sugar levels, poor circulation, and infections. It commonly affects the feet and lower extremities, posing serious risks if left untreated. Orthopedic Treatment for Diabetic Gangrene plays a critical role in preventing amputation and ensuring a structured recovery process. This article explores how orthopedic specialists manage diabetic gangrene, from infection control to rehabilitation, and highlights the best practices for prevention and long-term recovery.
Understanding Diabetic Gangrene
Orthopedic Treatment for Diabetic Gangrene begins with a thorough understanding of the condition. Diabetic gangrene occurs when a lack of blood flow leads to tissue death, often resulting in infection. High glucose levels in diabetics create an environment where bacteria thrive, making infections more aggressive. Symptoms include discoloration, foul-smelling discharge, numbness, and severe pain in the affected area. Identifying these early warning signs can significantly improve treatment outcomes and prevent the spread of gangrene.
The Role of Orthopedic Treatment in Diabetic Gangrene
Orthopedic specialists play a crucial role in managing diabetic gangrene by evaluating the severity of tissue damage and determining the best course of action. Orthopedic Treatment for Diabetic Gangrene involves a multidisciplinary approach, integrating endocrinologists, vascular surgeons, and wound care experts. Diagnostic tools such as X-rays, MRIs, and blood tests help assess the depth of infection and guide treatment decisions. The primary goal of orthopedic intervention is to preserve as much healthy tissue as possible while eliminating infected areas.
Infection Control Strategies
The first step in Orthopedic Treatment for Diabetic Gangrene is infection control. Since bacterial infections can rapidly deteriorate the condition, aggressive antibiotic therapy is often required. Broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed initially, followed by targeted medications based on culture results. Orthopedic specialists may recommend surgical debridement, a procedure that removes dead tissue to prevent the infection from spreading. Advanced wound care techniques, such as negative pressure wound therapy and hyperbaric oxygen therapy, accelerate healing and improve circulation, reducing the risk of amputation.
Surgical Interventions for Severe Cases
In cases where infection control alone is insufficient, Orthopedic Treatment for Diabetic Gangrene may require surgical interventions. Limb-salvaging procedures, such as vascular bypass surgery, aim to restore blood flow and prevent further tissue damage. However, when the infection is widespread, amputation may be the only viable option to save the patient’s life. Orthopedic specialists carefully assess the extent of gangrene before recommending amputation, considering prosthetic options and post-surgical rehabilitation to enhance mobility and quality of life.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Post-surgical recovery is a crucial aspect of Orthopedic Treatment for Diabetic Gangrene. Physical therapy plays a vital role in helping patients regain mobility and strength, particularly after amputation. Orthopedic specialists work closely with rehabilitation teams to ensure patients receive customized exercises that prevent muscle atrophy and promote circulation. Additionally, managing diabetes effectively is essential for long-term recovery. Proper blood sugar control, a balanced diet, and medication adherence significantly reduce the risk of recurrence. Patients are also advised on foot care routines, including daily inspections and appropriate footwear, to prevent future complications.
Preventing Diabetic Gangrene: Key Orthopedic and Lifestyle Tips
Preventive measures are an integral part of Orthopedic Treatment for Diabetic Gangrene. Regular foot screenings allow early detection of ulcers and infections, reducing the chances of developing gangrene. Wearing properly fitted shoes that reduce pressure points minimizes injury risks. Patients are encouraged to follow wound care best practices, such as keeping the feet clean and dry, applying antiseptic solutions, and avoiding barefoot walking. Moreover, maintaining stable blood sugar levels supports overall vascular health, reducing the likelihood of severe complications.
Takeaway
Timely Orthopedic Treatment for Diabetic Gangrene can make a significant difference in preserving limb function and improving quality of life. Early infection control, effective surgical interventions, and a structured rehabilitation plan ensure better outcomes for diabetic patients. By adopting preventive strategies, managing diabetes, and following orthopedic recommendations, individuals can significantly lower their risk of developing diabetic gangrene. Seeking immediate medical attention at the first sign of infection is crucial for successful treatment and long-term health management.