Diabetes often brings a host of complications, with foot ulcers being one of the most serious challenges faced by those with the condition. When foot ulcers develop, prompt and specialized care is essential. This article explores the critical role of orthopedic treatment in managing foot ulcers caused by diabetes, with a detailed discussion on infection control, tissue preservation, and improving mobility for enhanced healing outcomes.
Understanding the Connection: Diabetes and Foot Ulcers
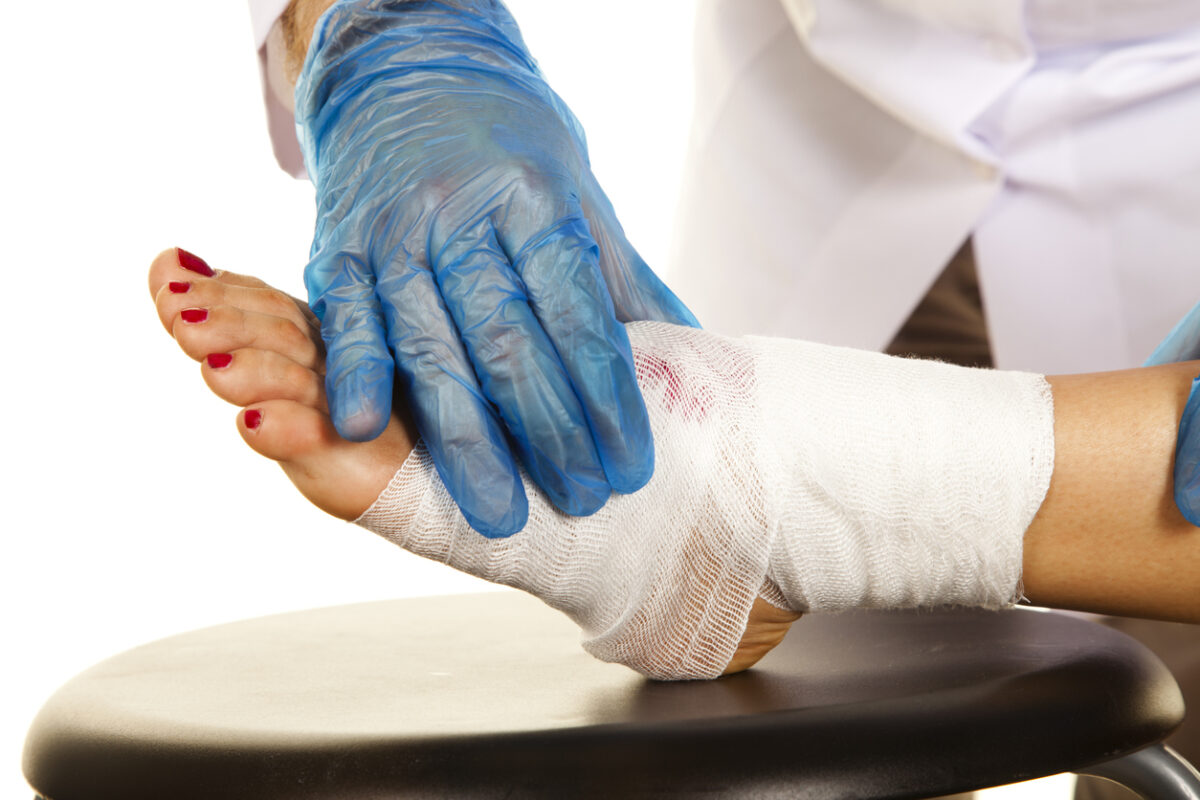
Foot ulcers are open sores or wounds that frequently appear on the bottom of the feet. For people living with diabetes, these wounds can develop due to a combination of factors such as impaired circulation and nerve damage (neuropathy). Neuropathy reduces the ability to sense pain, meaning minor injuries can go unnoticed and develop into severe ulcers.
Diabetes and Its Impact on Foot Health: Diabetes impacts blood vessels and nerves, leading to compromised blood flow. Poor circulation means that even a small cut or blister may struggle to heal properly, increasing the likelihood of infection. Additionally, the lack of proper sensory feedback makes it difficult for patients to detect injuries early, which is why preventive care is so important. Over time, unchecked foot ulcers can lead to more serious complications, including amputations, if infections spread or the tissue becomes severely damaged.
The Role of Orthopedics in Managing Foot Ulcers
Orthopedic treatment offers a specialized approach to address the complexities associated with foot ulcers in diabetic patients. Focusing on the structural integrity of the foot, orthopedic interventions address not only the wound itself but also the underlying mechanical and circulatory issues that contribute to their formation.
Why Orthopedic Treatment is Essential: Early intervention by orthopedic specialists can prevent the progression of a seemingly simple ulcer into a more complicated condition. The treatment is designed to:
- Control and eliminate infections: Quick diagnosis and treatment of infections are critical in avoiding further tissue damage.
- Preserve healthy tissue: Techniques are employed to prevent the spread of damage to surrounding areas, ensuring that as much healthy tissue as possible remains intact.
- Improve mobility: By addressing the mechanical issues that affect the foot, orthopedic treatment helps maintain or restore mobility, which is crucial for overall health and quality of life.
Orthopedic treatment for foot ulcers caused by diabetes is not solely focused on wound care; it is an integrated approach that deals with the root causes of the ulcers.
Components of a Specialized Orthopedic Treatment Approach
A comprehensive treatment plan for diabetic foot ulcers combines various aspects of care to ensure the best outcomes for patients. This multidisciplinary approach typically involves the following key components:
Infection Management: Effective management of infections is the cornerstone of orthopedic treatment for foot ulcers caused by diabetes. Since diabetic patients are more susceptible to infections due to compromised blood flow, a proactive strategy is crucial. The steps involved in infection management include:
- Early Diagnosis: Rapid assessment through clinical examinations and laboratory tests (including cultures and imaging studies) to determine the type and severity of the infection.
- Antibiotic Therapy: Tailored antibiotic regimens based on culture sensitivity tests help in eliminating the infection with minimal side effects.
- Debridement: This process involves the careful removal of dead or infected tissue, which helps in reducing bacterial load and promotes the healing process. Both surgical and non-surgical debridement techniques may be employed depending on the severity of the case.
- Wound Care Techniques: Utilization of advanced wound dressings, negative pressure wound therapy, and bioengineered tissue options can expedite healing by maintaining a moist wound environment while preventing external contamination.
Tissue Preservation: Preserving healthy tissue during treatment is essential to ensure proper recovery and reduce future complications. Orthopedic specialists employ several strategies to maximize tissue preservation:
- Precision in Surgical Procedures: When surgery is necessary, minimally invasive techniques are preferred to reduce collateral damage and preserve as much healthy tissue as possible.
- Use of Regenerative Medicine: Some treatments involve regenerative therapies that stimulate the body’s natural healing processes. This can include the application of growth factors or stem cell therapies aimed at repairing damaged tissues.
- Monitoring and Follow-Up: Continuous monitoring of the wound enables early identification of any new tissue degradation or infection, ensuring that prompt action can be taken to preserve tissue integrity.
Improving Mobility and Enhancing Healing: Restoring and maintaining mobility is a critical aspect of managing diabetic foot ulcers. The orthopedic approach involves:
- Rehabilitation Programs: Tailored physical therapy programs help patients regain strength and mobility. These programs are designed to adjust to the individual’s needs and may include exercises to improve balance, strength, and flexibility.
- Orthotic Devices: Custom footwear or orthotic devices can alleviate pressure on the ulcerated area, reducing pain and preventing further injury. These devices are specifically engineered to support the foot structure while ensuring proper alignment.
- Patient Education: Educating patients about proper foot care and the importance of regular movement prevents pressure build-up in vulnerable areas. Guidance on lifestyle modifications, including appropriate physical activity and dietary management, is also an integral part of this process.
Preventive Measures and Home Care Tips
While professional medical intervention is crucial, patients can also adopt preventive measures to minimize the risk of developing foot ulcers. Some effective strategies include:
- Regular Self-Examination: Daily inspection of the feet is essential. Any cuts, blisters, or abnormalities should be reported to a healthcare provider immediately.
- Proper Foot Hygiene: Maintaining clean and moisturized feet, while avoiding overly tight footwear, can prevent the onset of ulcers. Ensuring that the feet are dried thoroughly after washing helps avoid fungal infections.
- Blood Sugar Management: Consistently controlling blood sugar levels is vital for reducing the risk of complications. Patients should follow their medication regimen and dietary recommendations.
- Use of Protective Footwear: Wearing shoes that fit well and provide adequate support can prevent injuries. Additionally, patients may benefit from specially designed diabetic shoes that reduce friction and pressure points.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Engaging in regular physical activity, while taking precautions to protect the feet, helps improve circulation and overall health. A well-rounded approach to health that includes smoking cessation and a balanced diet also contributes to better outcomes.
A Comprehensive Look at the Path Forward
Orthopedic treatment for foot ulcers caused by diabetes is an essential aspect of managing one of the most challenging complications associated with the condition. The approach is multifaceted, addressing not only the wound itself but also the underlying issues such as impaired circulation and decreased mobility. By focusing on early infection management, preserving healthy tissue, and improving mobility, this specialized care aims to provide diabetic patients with the best possible chance for recovery and long-term health.
Patients and caregivers need to be aware of the symptoms and risk factors associated with foot ulcers. Recognizing early signs can make a substantial difference in the outcome. Awareness, combined with timely and appropriate orthopedic care, can prevent minor wounds from escalating into severe complications.
In addition, routine check-ups and education on self-care practices are invaluable. Health professionals play a pivotal role not only in the treatment of existing ulcers but also in providing guidance to help prevent future occurrences. Educational resources, support groups, and community programs can further empower patients to actively manage their foot health.
Takeaway
Managing foot ulcers in diabetic patients requires a comprehensive and proactive approach. Orthopedic treatment for foot ulcers caused by diabetes offers a specialized pathway that combines prompt infection management, tissue preservation, and techniques to enhance mobility. As a result, patients receive not only treatment for the ulcer but also an integrated plan that addresses the broader health challenges posed by diabetes.
Empowered by the right knowledge and effective treatment strategies, patients can achieve improved healing outcomes and a better quality of life. Early detection, ongoing care, and a commitment to preventive measures are essential to ensure that foot ulcers do not lead to more serious complications. For anyone facing the risks associated with diabetic foot ulcers, seeking timely orthopedic care can make all the difference, paving the way toward a healthier, more active future.
By embracing a holistic treatment strategy, healthcare providers are helping diabetic patients overcome some of the most daunting challenges of the condition. The integrated approach, which addresses both the immediate risks and the underlying causes, is vital for long-term recovery and improved mobility. This comprehensive care strategy not only helps to heal existing wounds but also plays a key role in preventing further complications, ensuring that patients can lead active, fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by diabetes.
Ultimately, the road to recovery begins with a commitment to quality care and ongoing education. Patients are encouraged to work closely with their healthcare teams, follow prescribed treatment plans, and adopt lifestyle changes that support overall foot health. With the right intervention, the complications of foot ulcers in diabetic patients can be managed effectively, fostering a future where challenges are met with robust, expert care.