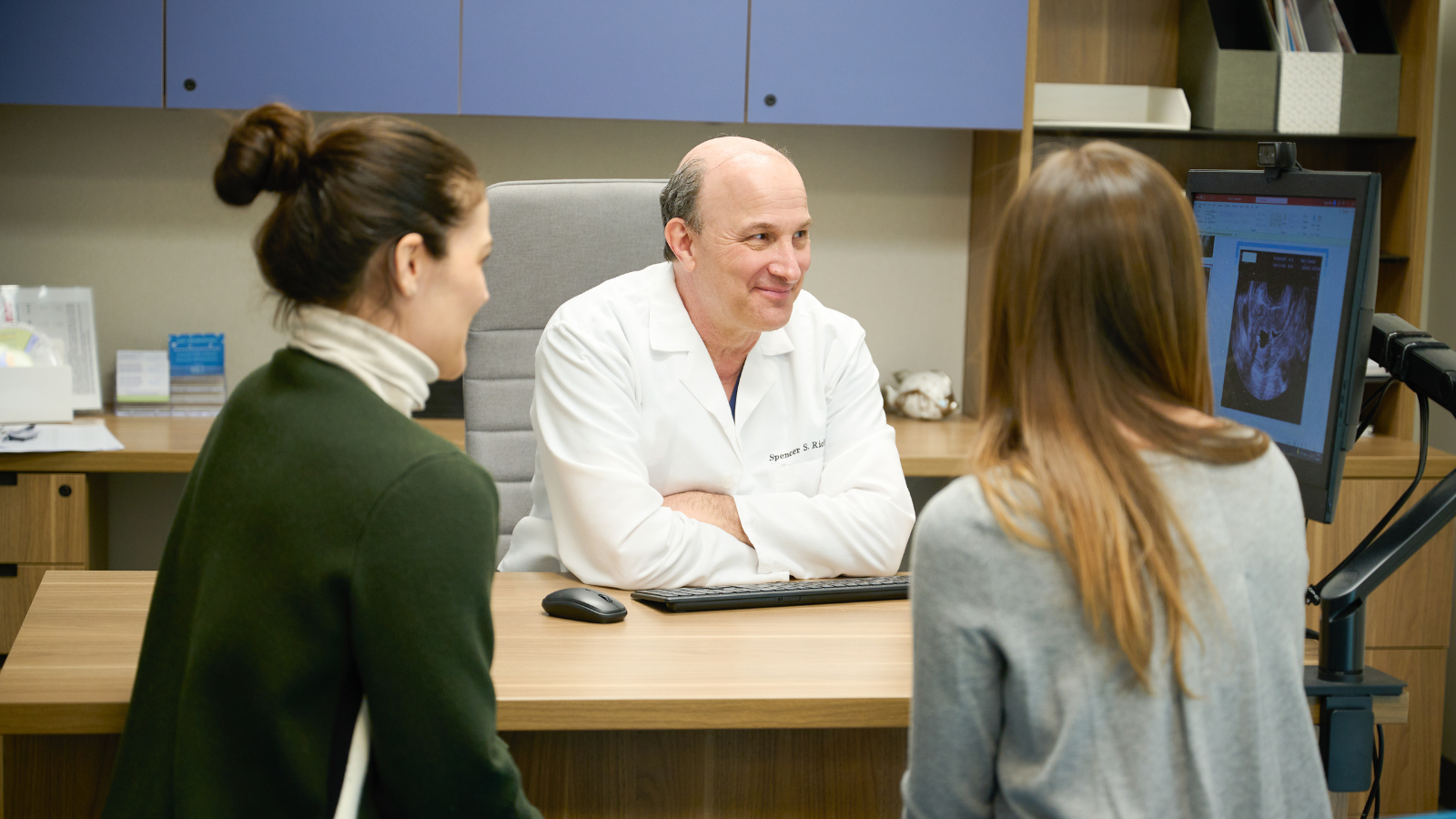
Understanding Reproductive Endocrinology and Infertility
Reproductive endocrinology and infertility is a specialized field that focuses on the interaction between hormones and reproductive health. Hormones act as chemical messengers that regulate the menstrual cycle, ovulation, sperm production, and overall reproductive function. Any disruption in hormone levels can significantly affect fertility, making early diagnosis and treatment essential. This field helps identify and manage conditions that prevent conception, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, and hormonal imbalances in men and women. Fertility issues often arise due to subtle hormonal changes that may go unnoticed until conception becomes difficult. Through careful evaluation, reproductive endocrinologists can pinpoint the exact hormonal disruptions causing fertility challenges. Understanding how hormones work together provides a foundation for personalized treatment strategies that improve reproductive outcomes.
Key Hormones That Influence Fertility
Several hormones play critical roles in fertility, each influencing different aspects of reproductive health. Estrogen is essential for ovulation and preparing the uterine lining to support a fertilized egg. Progesterone maintains the uterine environment during early pregnancy and regulates the menstrual cycle. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) control egg production, maturation, and release, forming the backbone of the ovulation process. Testosterone, though often associated with male fertility, is also important in female reproductive function, influencing libido and egg health. Thyroid hormones regulate metabolism and can affect menstrual regularity and ovulation. Prolactin, primarily known for lactation, can disrupt fertility when levels are too high. Maintaining a balanced hormonal profile ensures that the body can sustain conception, support early pregnancy, and optimize reproductive health.
Hormonal Imbalances and Fertility Challenges
Hormonal imbalances are among the leading causes of infertility. Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) result in elevated androgens, irregular ovulation, and reduced fertility. Thyroid disorders, including hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism, can alter menstrual cycles and interfere with egg quality. Hyperprolactinemia, or excessive prolactin levels, may prevent ovulation and reduce the chance of conception. Symptoms of hormonal imbalances include irregular periods, fatigue, unexplained weight changes, low libido, and difficulty conceiving. Diagnosis typically involves blood tests, ultrasound imaging, and hormone monitoring to determine the root cause of reproductive challenges. Once identified, these imbalances can often be treated with targeted therapies to restore fertility. Early intervention increases the likelihood of successful conception and healthy pregnancy outcomes.
Reproductive Endocrinology Treatments for Hormonal Regulation
Treatment in reproductive endocrinology focuses on restoring hormonal balance to improve fertility outcomes. Medical interventions may include hormone therapy, ovulation induction medications, or targeted fertility drugs. Assisted reproductive technologies, such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) and intrauterine insemination (IUI), are often recommended when natural conception is hindered by hormonal disruptions. Lifestyle changes, including diet, exercise, and stress management, can enhance hormone regulation and support reproductive health. Regular monitoring of hormone levels helps reproductive endocrinologists adjust treatments for optimal results. Some patients may also benefit from complementary approaches, such as nutritional supplementation or acupuncture, which can support hormonal balance. The goal is to create a personalized plan that addresses specific hormonal deficiencies and maximizes fertility potential.
Bullet List: Common Reproductive Endocrinology Treatments
- Ovulation induction using medications like clomiphene citrate or letrozole
- Hormone replacement therapy for estrogen or progesterone deficiencies
- Thyroid hormone regulation to correct hyper- or hypothyroidism
- Prolactin-lowering medications to restore ovulation
- Assisted reproductive technologies including IVF and IUI
- Lifestyle modifications to support hormone health
- Regular hormone monitoring and personalized treatment adjustments
Male Fertility and Hormonal Influence
Hormones are equally critical in male fertility, affecting sperm production, motility, and overall reproductive function. Testosterone is the primary male hormone, regulating libido, sperm development, and sexual function. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates sperm production in the testes, while luteinizing hormone (LH) triggers testosterone production. Hormonal imbalances in men can lead to low sperm count, poor motility, or impaired sperm quality, making conception more difficult. Causes of male hormonal infertility may include genetic factors, chronic illness, stress, obesity, or lifestyle habits. Reproductive endocrinologists use blood tests, semen analysis, and other diagnostic tools to identify hormonal deficiencies. Treatments often involve hormone therapy, lifestyle adjustments, or assisted reproductive technologies to improve fertility outcomes.
Emerging Research and Future Directions
Advances in reproductive endocrinology continue to improve understanding of hormone-related fertility challenges. Researchers are exploring personalized medicine approaches that tailor fertility treatments based on individual hormone profiles and genetic markers. New medications and therapies aim to precisely regulate hormone levels, increasing the success rates of natural conception and assisted reproductive technologies. Understanding the role of epigenetics provides insights into how environmental factors, lifestyle, and age can affect hormonal fertility. Minimally invasive procedures and advanced monitoring techniques allow reproductive endocrinologists to closely track hormone fluctuations for better outcomes. Male fertility research is also expanding, focusing on optimizing hormone levels and sperm quality. Ongoing innovation promises more effective, less invasive, and highly targeted solutions for couples struggling with hormone-related infertility.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What hormones are most important for fertility?
Key hormones include estrogen, progesterone, FSH, LH, testosterone, thyroid hormones, and prolactin. Each plays a distinct role in ovulation, sperm production, and reproductive health.
Can lifestyle changes improve hormone-related infertility?
Yes. Balanced nutrition, regular exercise, stress management, and maintaining a healthy weight can positively impact hormone regulation and fertility outcomes.
How long does it take to see results from hormone therapy?
The timeframe varies depending on the type of hormonal imbalance and the treatment used, but many patients notice improvements within a few menstrual cycles.
Are there risks associated with fertility medications?
Fertility medications can have side effects such as mood changes, bloating, or ovarian hyperstimulation. Doctors carefully monitor patients to minimize risks.
How do doctors test for hormonal imbalances in both men and women?
Hormonal imbalances are typically diagnosed through blood tests, urine tests, semen analysis, and imaging studies to evaluate reproductive organs and hormone levels.
Takeaway
The connection between hormones and fertility in reproductive endocrinology highlights the intricate interplay of chemical messengers that govern reproductive health. Understanding these hormones, identifying imbalances, and implementing targeted treatments can dramatically improve the chances of conception for both men and women. With advances in medical science and personalized care, reproductive endocrinology continues to offer hope for individuals and couples seeking to build families, emphasizing the critical role of hormones in every step of the fertility journey.