Wound infections can happen to anyone, whether from a minor scrape or a deeper injury. Knowing when to seek medical attention is vital to avoid complications and promote healing. A doctor for infected wounds plays a crucial role in diagnosing, treating, and managing infections to help patients recover quickly and safely. This article covers everything you need to know about infected wounds, how doctors handle them, and ways to care for wounds to prevent infections.
Understanding Infected Wounds: Causes and Risks
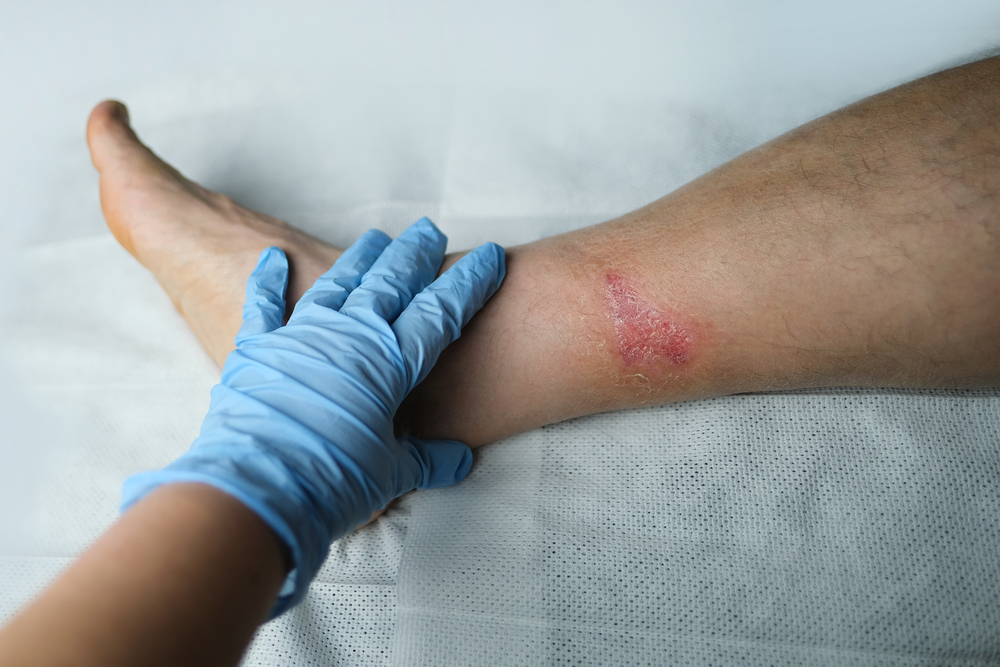
An infected wound occurs when harmful bacteria, viruses, or fungi invade an open injury, disrupting the normal healing process. These pathogens multiply and trigger inflammation, causing redness, swelling, pain, and sometimes pus formation. Common causes of wound infections include cuts, punctures, burns, surgical incisions, or animal bites that aren’t cleaned or treated properly. People with weakened immune systems, diabetes, or poor circulation are more vulnerable to infections because their bodies have a harder time fighting off germs. Other risk factors include exposure to contaminated environments and delayed wound care.
Without proper treatment, infected wounds may worsen, leading to severe complications such as cellulitis, abscesses, or even sepsis, a life-threatening condition. Understanding the risks behind an infected wound encourages timely medical intervention. Being aware of what makes an infection more likely can empower individuals to take the right precautions and seek help promptly. Identifying infection early prevents chronic wounds and supports faster recovery.
When to Seek a Doctor for Infected Wounds
Recognizing the warning signs of an infected wound can make all the difference. Typical symptoms include increased redness around the wound, swelling, warmth, pain that worsens over time, pus or foul-smelling discharge, and sometimes fever or chills. If any of these signs appear, it’s important to consult a doctor for infected wounds without delay. Not all wounds require medical attention, but when these symptoms persist or worsen, professional care is essential.
Minor cuts and abrasions often heal on their own with proper hygiene, but infections change the situation significantly. Delaying treatment can allow bacteria to spread deeper into tissues or bloodstream, increasing the risk of complications. If you notice the wound is not healing after a few days or if symptoms intensify, make an appointment with a healthcare provider. Timely evaluation and care not only stop the infection from progressing but also reduce pain and improve outcomes.
Doctors are trained to assess wounds for severity and determine the best treatment approach. Early professional intervention helps avoid emergency situations, hospitalizations, and surgeries that sometimes become necessary if infections are neglected. Understanding when to see a doctor for infected wounds supports better health decisions and safer healing.
Role of a Doctor in Treating Infected Wounds
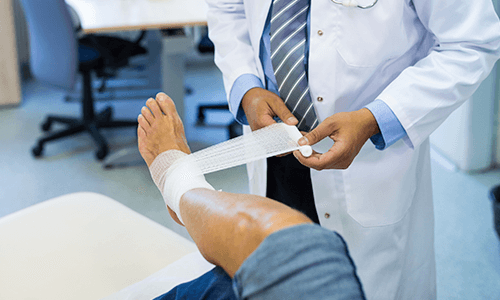
A doctor for infected wounds is equipped with the knowledge and tools needed to provide comprehensive care. This may include general practitioners, wound care specialists, or surgeons depending on the wound’s nature and severity. The first step in treatment is a thorough evaluation, which involves visually inspecting the wound and possibly taking a sample or swab to identify the infectious agents. In some cases, imaging tests like X-rays help determine if the infection has spread to deeper tissues or bones.
Once the infection is confirmed, doctors usually prescribe antibiotics either orally or topically to fight the bacteria. The choice of medication depends on the type of bacteria, wound location, and patient health factors. In more serious cases, wound cleaning procedures such as debridement—removal of dead or infected tissue—may be necessary to promote healing. For infections that have spread extensively, hospitalization and intravenous antibiotics might be required.
Doctors also guide patients on wound care practices, including how to clean and dress the wound properly. Monitoring progress through follow-up visits ensures that the infection is resolving and the wound is healing. This medical supervision reduces the risk of further complications and supports overall recovery.
Advanced Medical Treatments and Technologies for Infected Wounds
Recent advancements in wound care have introduced innovative treatments that enhance the healing process for infected wounds. Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), also known as a wound vacuum, uses controlled suction to remove fluids and promote tissue regeneration. This technique can be highly effective for large or chronic infected wounds. Specialized dressings containing antimicrobial agents are also widely used to keep the wound environment clean and reduce infection risk.
Antibiotic treatment is more targeted now thanks to lab tests that identify specific bacteria strains. This allows doctors to prescribe the most effective drugs, reducing the chances of antibiotic resistance and speeding up recovery. Topical antibiotics can deliver medication directly to the wound, minimizing systemic side effects.
Newer technologies also include bioengineered skin substitutes and growth factors that stimulate tissue repair. These treatments, often used in combination with standard care, offer hope for patients with complicated infections or wounds that are slow to heal. With ongoing research and innovation, the options for managing infected wounds continue to improve.
At-Home Care Guidance from Doctors for Wound Infection Recovery
Doctors emphasize the importance of proper at-home care alongside medical treatment to ensure a full recovery from an infected wound. Keeping the wound clean and dry, changing dressings regularly, and avoiding irritation are key components of home care. Patients are advised to wash hands thoroughly before handling wounds to prevent introducing new bacteria.
Monitoring the wound daily helps catch any signs of worsening infection early. If symptoms like increased redness, swelling, pain, or discharge reappear, a prompt return visit to the doctor is crucial. Hydration, balanced nutrition, and rest support the body’s ability to heal.
Doctors often recommend avoiding smoking and controlling underlying conditions such as diabetes during recovery since these factors can delay wound healing. Following the prescribed antibiotic course fully, even if symptoms improve, is vital to prevent infection recurrence. Maintaining good communication with the healthcare provider ensures any concerns are addressed quickly, helping to avoid setbacks.
Preventing Wound Infections: Medical Advice and Best Practices
Prevention plays a major role in avoiding wound infections, and doctors provide valuable guidance to minimize risks. Proper wound cleaning immediately after injury involves gently rinsing with clean water and using sterile dressings. Avoiding harsh chemicals or unproven remedies helps protect sensitive tissue. Covering wounds appropriately prevents contamination from dirt and bacteria.
Vaccinations, such as tetanus shots, are essential for individuals with certain types of wounds to prevent serious infections. People with chronic conditions like diabetes should work closely with healthcare providers to maintain good blood sugar control, which is critical for wound healing. Lifestyle choices such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking improve immune function and skin integrity.
Doctors encourage patients to recognize signs of infection early and not ignore wounds that fail to heal. Routine check-ups and wound evaluations ensure any issues are caught before they become serious. Taking these preventive steps reduces the need for more intensive treatments and supports long-term health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How quickly should I see a doctor if I suspect my wound is infected?
Seek medical care as soon as you notice symptoms such as increased redness, swelling, warmth, pain, pus, or fever. Early treatment is key to preventing complications.
Can all infected wounds be treated without surgery?
Many infected wounds respond well to antibiotics and proper wound care. Surgery is typically reserved for severe infections or when dead tissue needs removal.
What complications can arise if an infected wound is left untreated?
Untreated infections can lead to cellulitis, abscess formation, systemic infections like sepsis, delayed healing, or permanent tissue damage.
Are there specific antibiotics commonly prescribed for wound infections?
The choice depends on the bacteria involved. Common antibiotics include cephalexin, clindamycin, and amoxicillin-clavulanate, but a doctor will tailor treatment based on testing.
How can I reduce scarring after wound infection treatment?
Following wound care instructions, keeping the wound moist with appropriate dressings, and protecting the area from sun exposure can minimize scarring. Your doctor may also recommend specialized creams or treatments.