Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) are one of the most serious complications faced by individuals with diabetes. These wounds not only reduce quality of life but can also lead to infections, hospitalization, and even amputation if left untreated. Comprehensive diabetic foot ulcer management is essential to prevent progression, improve healing outcomes, and reduce recurrence. Understanding the underlying causes, implementing early interventions, and maintaining ongoing care are crucial elements in effectively managing DFUs. Patients, caregivers, and healthcare providers all play critical roles in ensuring that these wounds receive appropriate attention and treatment.
Understanding Diabetic Foot Ulcers
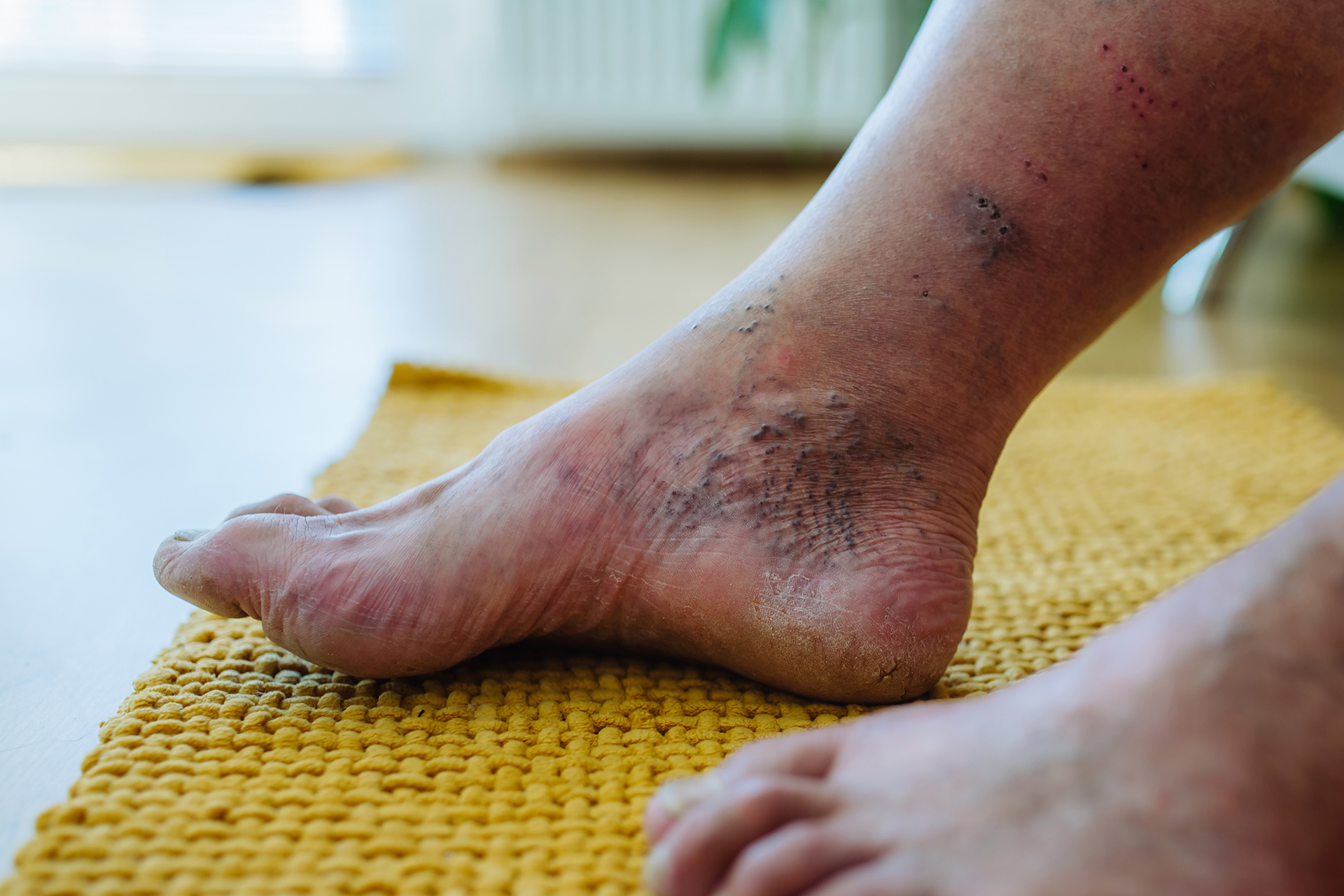
Diabetic foot ulcers are open sores or wounds that most commonly occur on the bottom of the foot. They develop due to a combination of factors including neuropathy (nerve damage), poor circulation, and immune system deficiencies. Neuropathy reduces the ability to feel pain, pressure, or temperature changes, making injuries more likely to go unnoticed. Poor circulation further slows the healing process and increases the risk of infection. These ulcers are categorized into neuropathic, ischemic, and neuroischemic types, each requiring specific treatment approaches. Early identification of DFUs is critical because minor injuries can quickly escalate into complex wounds. Educating patients about recognizing early signs like redness, calluses, or small cuts can significantly improve outcomes. Comprehensive diabetic foot ulcer management begins with a deep understanding of these risk factors and preventive measures.
Risk Assessment and Screening
A key component of comprehensive diabetic foot ulcer management is regular risk assessment. Patients with long-term diabetes, poor glycemic control, or comorbidities such as peripheral artery disease are at higher risk. Routine foot examinations should be conducted at every clinical visit, focusing on skin integrity, nail health, deformities, and signs of infection. Screening tools, such as the monofilament test, help identify patients with reduced sensation. High-risk patients should be monitored more frequently to detect potential issues before ulcers form. Educating patients on self-inspection techniques encourages early detection and timely intervention. By integrating risk assessment and proactive screening, healthcare providers can reduce the severity of diabetic foot ulcers and prevent complications.
Medical and Therapeutic Approaches
Effective management of diabetic foot ulcers involves medical and therapeutic strategies tailored to individual patient needs. Maintaining optimal glycemic control is fundamental, as high blood sugar impairs wound healing and increases infection risk. Topical treatments, including advanced dressings, antimicrobial creams, and growth factors, promote tissue regeneration. Systemic interventions, such as targeted antibiotics, are essential when infection is present. Offloading the affected area through specialized footwear, orthotics, or total contact casting reduces pressure on the ulcer and accelerates healing. Physical therapy may also be recommended to improve circulation and maintain mobility. Comprehensive diabetic foot ulcer management emphasizes a personalized approach, ensuring patients receive both preventive care and active treatment to achieve optimal outcomes.
Advanced Wound Care Technologies
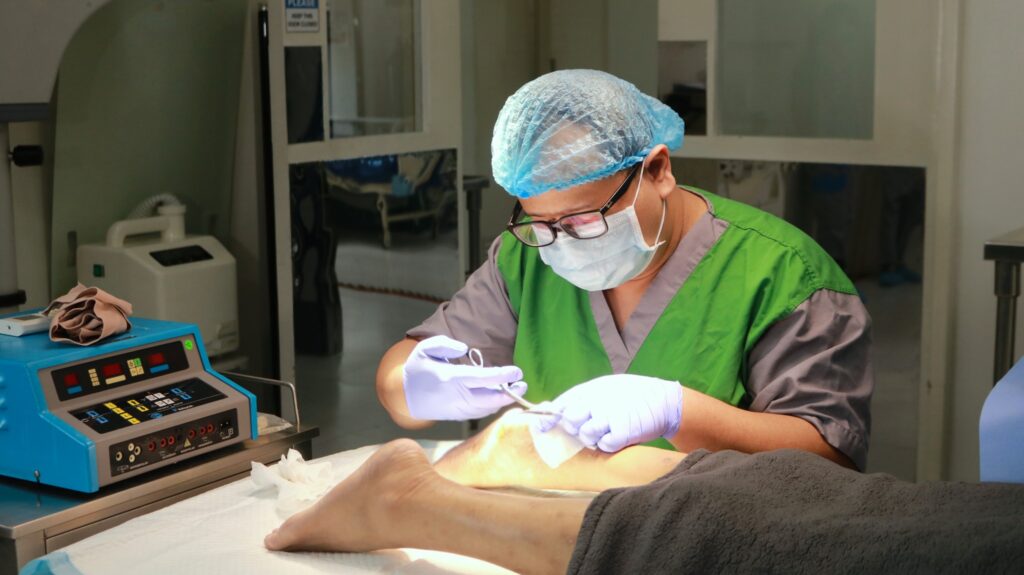
Modern technologies have transformed diabetic foot ulcer management, offering tools that improve healing rates and reduce complications. Debridement, which involves removing dead tissue, can be performed surgically, enzymatically, or autolytically, depending on the wound’s condition. Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) uses suction to remove excess fluid and stimulate tissue growth, while hyperbaric oxygen therapy enhances oxygen supply to damaged tissue, promoting recovery. Innovative dressings infused with silver, hydrocolloids, or bioengineered materials create an optimal healing environment. These advanced interventions, combined with proper medical care, support comprehensive diabetic foot ulcer management and reduce the likelihood of infection or recurrence. Staying updated on technological advancements enables healthcare providers to offer evidence-based, effective treatments.
Infection Prevention and Management
Infection is a major concern in diabetic foot ulcers and can rapidly escalate if not addressed. Common pathogens include Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas species, which require prompt identification and targeted antibiotic therapy. Signs of infection include increased redness, swelling, warmth, and foul odor from the wound. Preventive strategies, such as proper foot hygiene, daily inspection, and regular dressing changes, are essential. Patients should be educated on recognizing early infection symptoms and seeking medical attention promptly. For severe infections, hospitalization or surgical intervention may be necessary to prevent systemic complications. Comprehensive diabetic foot ulcer management integrates infection control at every stage to safeguard patient health and promote healing.
Patient Education and Lifestyle Management
Patient education is a cornerstone of diabetic foot ulcer management. Teaching individuals about proper foot hygiene, daily inspection, and nail care empowers them to take an active role in prevention. Lifestyle factors, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and blood sugar control, significantly impact wound healing. Patients should understand the importance of adhering to prescribed treatments and attending follow-up appointments. Stress management and smoking cessation also play supportive roles in improving circulation and reducing risk. Comprehensive diabetic foot ulcer management emphasizes that proactive self-care and healthy lifestyle choices are critical to preventing complications and improving long-term outcomes.
Multidisciplinary Approach
Managing diabetic foot ulcers requires collaboration among multiple healthcare professionals. Podiatrists, endocrinologists, wound care nurses, and physical therapists each contribute specialized expertise to patient care. A multidisciplinary approach ensures accurate diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and coordinated interventions. Regular communication between providers facilitates timely adjustments in therapy and promotes continuous monitoring. Rehabilitation services may support mobility, enhance circulation, and reduce the risk of secondary complications. Incorporating a team-based strategy reflects the essence of comprehensive diabetic foot ulcer management, where combined expertise leads to improved patient outcomes and enhanced quality of life.
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Treatment
Tracking the healing progress of diabetic foot ulcers is essential for effective management. Clinicians measure wound size, depth, exudate, and tissue quality to determine treatment efficacy. If healing is delayed or complications arise, adjustments may include advanced therapies, surgical debridement, or referral to specialized care centers. Regular documentation ensures continuity of care and allows for early identification of treatment failures. Comprehensive diabetic foot ulcer management relies on dynamic treatment plans that respond to patient progress. Continuous monitoring reinforces accountability and improves overall healing rates, reducing the likelihood of chronic wounds or amputations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How long does it typically take for a diabetic foot ulcer to heal?
Healing time varies depending on ulcer severity, patient health, and adherence to treatment. Minor ulcers may heal in a few weeks, while complex or infected wounds may take months. Comprehensive management and regular monitoring significantly reduce healing time.
2. Can diabetic foot ulcers be completely prevented?
While prevention is not always guaranteed, proper foot care, regular check-ups, and early risk assessment greatly reduce the likelihood of ulcers developing. Maintaining blood sugar control and using protective footwear are critical preventive measures.
3. What is the role of diet in managing diabetic foot ulcers?
Nutrition plays a key role in wound healing. A balanced diet rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals supports tissue repair and immune function. Proper blood sugar management through diet also reduces complications.
4. Are there home care strategies that effectively complement medical treatment?
Yes. Daily foot inspections, gentle cleaning, avoiding walking barefoot, and keeping feet dry help prevent infection. Offloading devices and following treatment plans prescribed by healthcare providers are also essential.
5. When should a patient seek urgent medical attention for a foot ulcer?
Immediate medical attention is necessary if there are signs of infection, worsening pain, foul odor, or sudden changes in wound appearance. Prompt care prevents complications such as sepsis or gangrene.