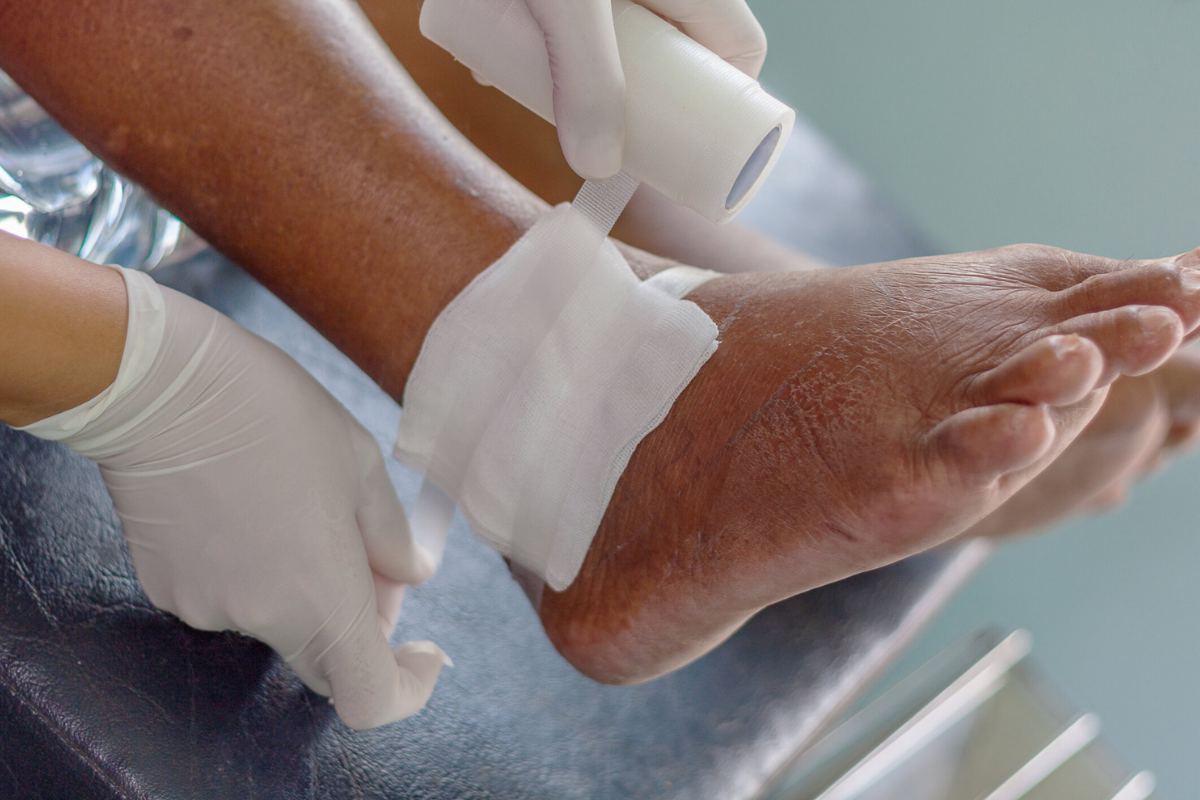
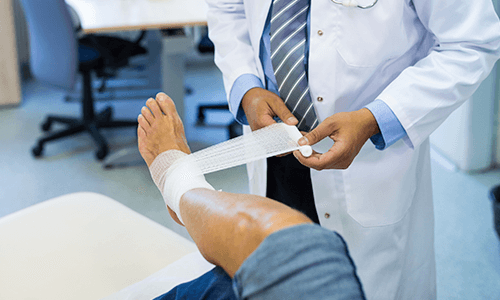
Understanding Non-Healing Wounds and Why They Matter
When a wound fails to heal after weeks of standard care, it may be considered a non-healing or chronic wound. Unlike minor cuts or scrapes that close naturally within days, these wounds linger, often worsening over time. The underlying causes can range from diabetes and vascular disease to infections or repeated trauma. Poor circulation, nerve damage, and reduced immunity can make even small wounds extremely difficult to recover from. Left untreated, these wounds can lead to severe complications such as deep infections, tissue loss, and even amputation in extreme cases. This is why they require a specialized approach that looks beyond surface-level healing. Orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds addresses both the immediate wound and the musculoskeletal conditions that may be preventing it from closing properly.
The Link Between Orthopedic Health and Wound Healing
Many people are surprised to learn how closely bone and joint health are tied to wound recovery. Orthopedic conditions such as fractures, arthritis, or foot deformities can create pressure points that restrict proper circulation or place constant stress on specific areas of the body. For instance, diabetic foot ulcers often develop in individuals with foot abnormalities that cause uneven weight distribution. Limited mobility, whether from an injury or chronic orthopedic condition, also increases the risk of wounds persisting. When the body cannot move efficiently, pressure builds in certain areas, which may restrict oxygen and nutrient flow to the tissues. Orthopedic specialists evaluate these factors to identify the root cause of delayed healing. Without addressing the structural or mechanical contributors, even the most advanced wound care techniques may only provide temporary relief.
Advanced Orthopedic Treatments for Non-Healing Wounds
When standard care such as cleaning and basic dressings are not enough, orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds provides more advanced solutions. Surgical interventions are often considered, including wound debridement, which removes dead tissue to stimulate fresh healing. In severe cases, bone grafting or reconstructive surgery may be required to restore function and stability while promoting tissue recovery. Orthopedic surgeons may also use skin grafts or tissue flaps to cover large or complex wounds, ensuring better blood flow and faster healing. Another innovative option is negative pressure wound therapy, which uses suction to remove fluids and encourage tissue growth. Biologic dressings made from advanced materials or regenerative cells are also becoming more common, giving patients access to cutting-edge healing methods. These procedures are often combined with orthopedic correction of underlying issues, ensuring the wound has the best chance of long-term closure.
Non-Surgical Orthopedic Interventions That Support Healing
Not every patient requires surgery to achieve progress. Many non-surgical orthopedic treatments are designed to relieve pressure, support proper alignment, and improve circulation. Special wound dressings combined with supportive braces or splints can protect vulnerable areas from further injury. Orthotics or custom footwear are commonly used for patients with foot ulcers or deformities, especially those with diabetes. Immobilization through casts or braces may help keep a wound stable, allowing tissues to recover without disruption. Physical therapy plays an essential role by strengthening muscles, improving mobility, and enhancing blood flow. This not only speeds up wound recovery but also reduces the chances of recurrence. Additionally, orthopedic care often involves managing inflammation and pain, both of which can interfere with healing when left untreated. These non-surgical methods are particularly valuable for patients seeking effective treatment without undergoing invasive procedures.
The Role of Multidisciplinary Care in Treating Non-Healing Wounds
Orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds rarely happens in isolation. Instead, it works best as part of a multidisciplinary approach that combines different areas of medical expertise. Orthopedic surgeons often collaborate with vascular specialists, wound care nurses, physical therapists, and endocrinologists. This collaboration ensures that underlying issues such as poor circulation, infection, or uncontrolled diabetes are addressed alongside the orthopedic condition. For example, a patient with a diabetic foot ulcer may require both vascular intervention to restore blood flow and orthopedic correction to relieve pressure points. Personalized treatment plans are created to fit the individual’s needs, maximizing the chances of recovery. When multiple experts work together, patients benefit from a well-rounded strategy that prevents complications and supports long-term healing. This team-based approach has become a cornerstone of modern orthopedic wound management.
Lifestyle and Preventive Strategies to Support Orthopedic Healing
While advanced medical treatment is crucial, lifestyle choices and preventive care also play a major role in wound recovery. Nutrition is one of the most important factors, as protein, vitamins, and minerals support both tissue and bone healing. Patients are encouraged to eat a balanced diet that includes foods rich in vitamin C, zinc, and calcium. Proper footwear is essential, especially for individuals with diabetes or orthopedic deformities that place added stress on the feet. Regular exercise, tailored to the patient’s condition, can improve circulation and prevent wounds from recurring. At the same time, safe mobility strategies reduce the risk of creating new pressure injuries. Daily monitoring of wounds allows for early detection of problems, giving patients a better chance to address them before they become severe. Preventive strategies are often emphasized in orthopedic treatment, as avoiding complications is just as important as treating existing wounds.
Choosing the Right Orthopedic Specialist for Wound Care
Selecting the right specialist can make a major difference in recovery outcomes. Patients should look for an orthopedic doctor with experience in wound management, particularly when dealing with diabetic or trauma-related wounds. Board certification, hospital affiliations, and a track record of successful treatments are indicators of expertise. Before beginning treatment, patients should feel comfortable asking questions about the doctor’s approach, available procedures, and expected results. Some orthopedic clinics specialize in advanced wound care, offering technologies and therapies that may not be available in general practices. Patients should also consider whether the clinic provides a multidisciplinary environment where collaboration is encouraged. The right orthopedic specialist will not only treat the wound but also address the structural and mechanical issues that are preventing healing. This ensures that recovery is both faster and more sustainable.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What types of wounds usually require orthopedic treatment?
Wounds associated with fractures, joint complications, diabetic ulcers, surgical sites, or pressure injuries often require orthopedic intervention. When musculoskeletal issues contribute to poor healing, orthopedic care becomes essential.
2. How long does it take for non-healing wounds to improve with orthopedic care?
Healing time varies depending on the wound’s severity, the patient’s health condition, and the chosen treatment. Some wounds begin improving within weeks, while more complex cases may take several months.
3. Are surgical procedures always necessary for orthopedic wound treatment?
No. Many patients benefit from non-surgical options such as braces, orthotics, specialized dressings, and physical therapy. Surgery is only recommended when other methods are not sufficient.
4. Can orthopedic treatments prevent wounds from coming back?
Yes. By correcting underlying orthopedic issues, reducing pressure points, and improving mobility, these treatments significantly lower the risk of wound recurrence.
5. What’s the difference between seeing a wound care specialist and an orthopedic doctor?
A wound care specialist primarily focuses on treating the wound itself, while an orthopedic doctor addresses structural and musculoskeletal causes that may be preventing healing. Both are often needed for complete recovery.
6. Does insurance typically cover orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds?
Many insurance plans do cover orthopedic wound care, especially when it is medically necessary. Patients should check with their providers to confirm coverage and understand any out-of-pocket costs.